# 208. Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)
Question link is here.
# Question
A trie (pronounced as "try") or prefix tree is a tree data structure used to efficiently store and retrieve keys in a dataset of strings. There are various applications of this data structure, such as autocomplete and spellchecker.
Implement the Trie class:
Trie()Initializes the trie object.void insert(String word)Inserts the stringwordinto the trie.boolean search(String word)Returnstrueif the stringwordis in the trie (i.e., was inserted before), andfalseotherwise.boolean startsWith(String prefix)Returnstrueif there is a previously inserted stringwordthat has the prefixprefix, andfalseotherwise.
Example 1:
Input
["Trie", "insert", "search", "search", "startsWith", "insert", "search"]
[[], ["apple"], ["apple"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"]]
Output
[null, null, true, false, true, null, true]
Explanation
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple"); // return True
trie.search("app"); // return False
trie.startsWith("app"); // return True
trie.insert("app");
trie.search("app"); // return True
# Solution
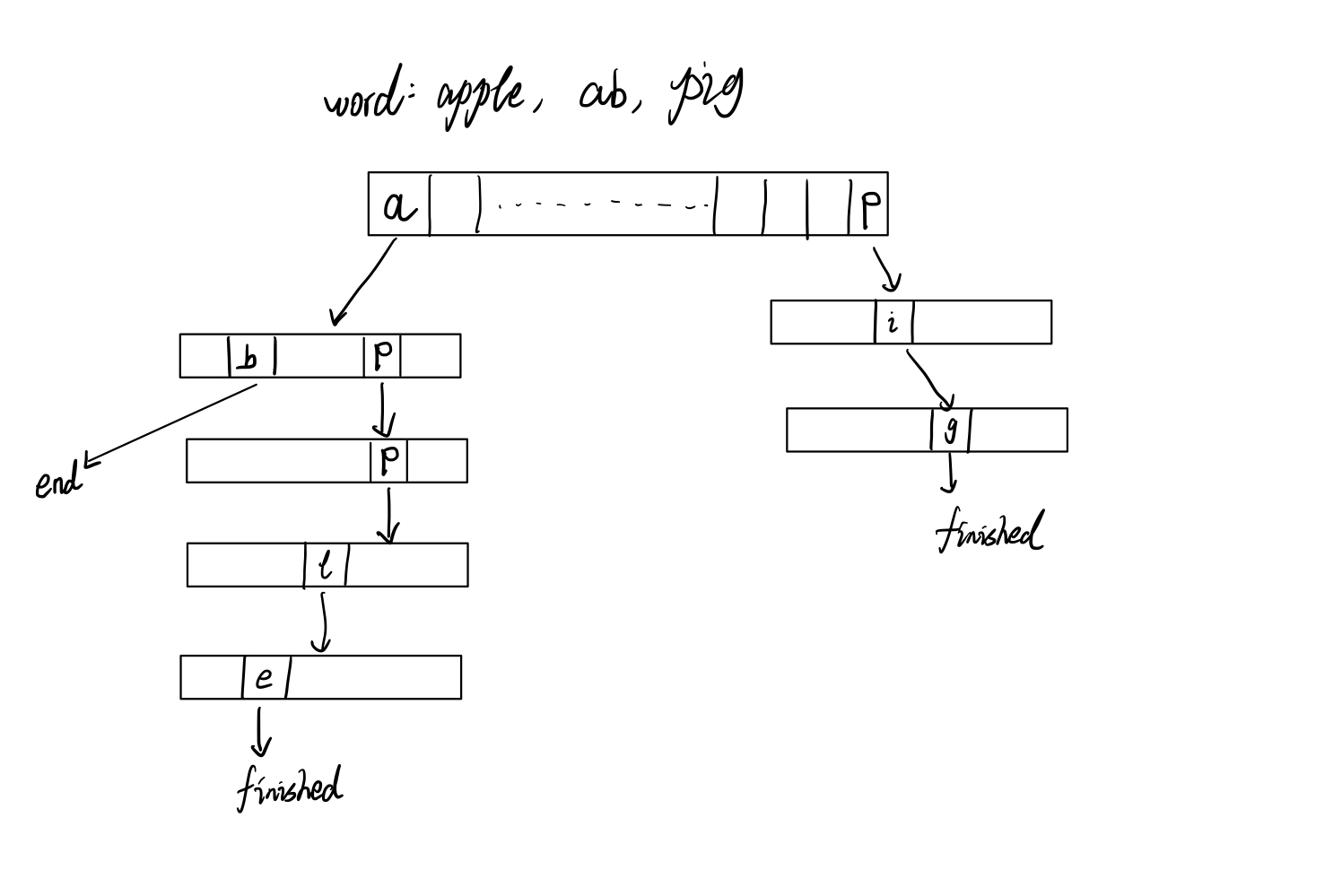
Each node contains 26 slots for for each char in the alphabet. Which means if slot[0] is not None, there is an 'a' in the current level of the tree. So when can follow the path to find if there exists a word.
And when a word ends, the next node is set to finished.
# Java
class Node {
Node[] lists;
boolean finished;
public Node() {
lists = new Node[26];
finished = false;
}
public void insert(char ch, Node node) {
lists[ch - 'a'] = node;
}
public boolean hasChar(char ch) {
return lists[ch - 'a'] != null;
}
public Node get(char ch) {
return lists[ch - 'a'];
}
public void setFinished(boolean b) {
finished = b;
}
}
class Trie {
Node root;
public Trie() {
root = new Node();
}
public void insert(String word) {
Node node = root;
for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
if (! node.hasChar(word.charAt(i))) {
node.insert(word.charAt(i), new Node());
}
node = node.get(word.charAt(i));
}
node.setFinished(true);
}
public Node searchHelper(String word) {
Node node = root;
for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
if(node.hasChar(word.charAt(i))) {
node = node.get(word.charAt(i));
} else {
return null;
}
}
return node;
}
public boolean search(String word) {
Node node = searchHelper(word);
if(node != null && node.finished == true)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
Node node = searchHelper(prefix);
if(node != null)
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie obj = new Trie();
* obj.insert(word);
* boolean param_2 = obj.search(word);
* boolean param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix);
*/
# Python
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.next = [None] * 26
self.finished = False
def hasChar(self, char):
if self.next[ord(char) - ord('a')] is not None:
return True
else:
return False
def insert(self, char, node):
self.next[ord(char) - ord('a')] = node
def get(self, char):
return self.next[ord(char) - ord('a')]
def setFinished(self, b):
self.finished = b
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.root = Node()
def insert(self, word: str) -> None:
node = self.root
for c in word:
if not node.hasChar(c):
node.insert(c, Node())
node = node.get(c)
node.setFinished(True)
def searchHelper(self, word):
node = self.root
for c in word:
if node.hasChar(c):
node = node.get(c)
else:
return None
return node
def search(self, word: str) -> bool:
node = self.searchHelper(word)
if node is not None and node.finished is True:
return True
else:
return False
def startsWith(self, prefix: str) -> bool:
node = self.searchHelper(prefix)
if node is not None:
return True
else:
return False
Time Complexity for each operations.